
Chinese Sixth Generaiton Fighter, Iranian Missiles Over Israel, Ukrainain Drone Strike on Tu-95s, Colombian Contractor in Ukraine
Military Watch Magazine Editorial Staff
January-1st-2026
The year 2025 saw the intensification of conflicts across multiple theatres, and the outbreak of new hostilities in Latin America, the Middle East, South and Southeast Asia, while major developments in ongoing arms races have shifted consensus among analysts regarding long term power trajectories affecting several key hotspots. As many of the conflicts, weapons programs, and military operations launched in 2025 are expected to continue into 2026, and as the possibility for new wars in a greater number of theatres continues to grow, an assessment of the the significant military developments of the past year provides vital context to understanding prevailing trends in international security and predicting how they may evolve. The ten most significant of 2025 are summarised below.
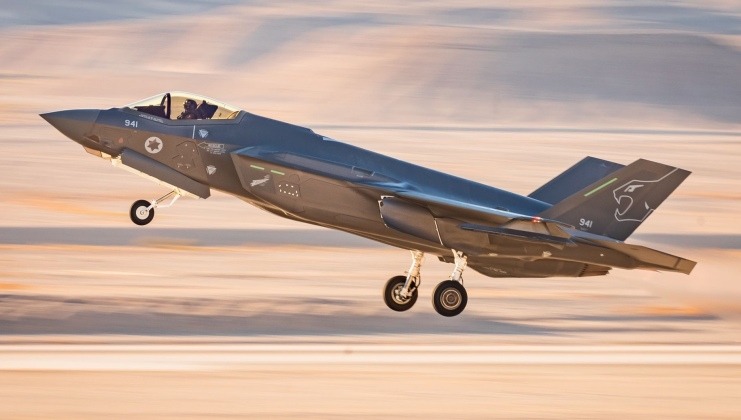

Israeli Air Force F-35I Fifth Generation Fighter
Israel and the United States Go to War with Iran: Retaliatory Missile Barrages Force End to Hostilities
On June 13 the Israel Defence Forces launched a large scale assault on targets across Iran, including military facilities, critical infrastructure, the country’s military and political leadership, and civilian nuclear sites. The campaign was heavily supported by Israeli strategic partners in the Western world, and made extensive use of Western- and Israeli-backed paramilitary groups on the ground to attack high value Iranian targets in coordination with air operations. Although the performance of Iranian conventional forces remained poor, the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps delivered the largest series of ballistic missile attacks in history, causing tremendous damage across Israel. Commenting on the damage, U.S. President Donald Trump observed: “Especially those last couple of days, Israel was hit really hard. Those ballistic missiles, boy they took out a lot of buildings.”
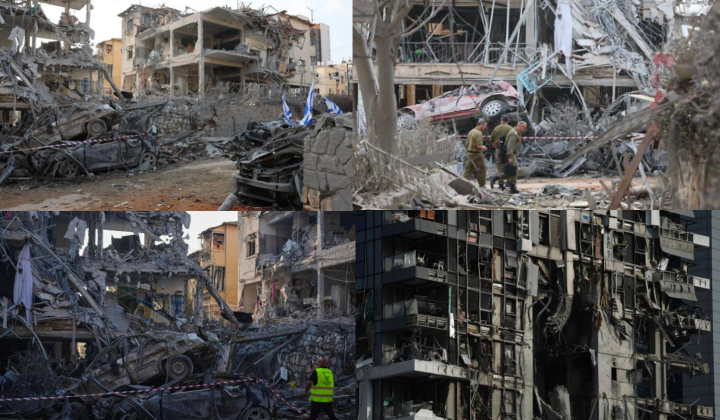

Damage in Tel Aviv After Iranian Missile Attacks
The U.S. Army expended over 25 percent of its total THAAD anti-ballistic missile arsenal during the 11 day period, costing $2.35 billion, alongside the multi-billion dollar costs of expending SM-3 and SM-6 anti-ballistic missiles from the U.S. Navy’s AEGIS destroyers, and several billion more in missiles fired by Israeli systems. Iran’s Fattah hypersonic ballistic missile made its combat debut in the conflict, and reportedly proved capable of bypassing all Israeli and U.S. air defences, leading Israeli defence planners to highlight the need to develop new countermeasures.
On the final day of hostilities the U.S. Air Force’s B-2 bombers for the first time demonstrated their ability to strike heavily fortified targets using GBU-57 bombs. The extensive damage caused by Iranian ballistic missile attacks has been widely assessed to be the primary factor leading Israel and the Untied States to cease their attacks short of overthrowing the Iranian government. Unconfirmed reports in September indicated that Iran was strengthening its air defences by acquiring MiG-29 fighters from Russia, and it was subsequently confirmed that Iran had ordered 48 Russian Su-35S fighters to further strengthen its air defences.
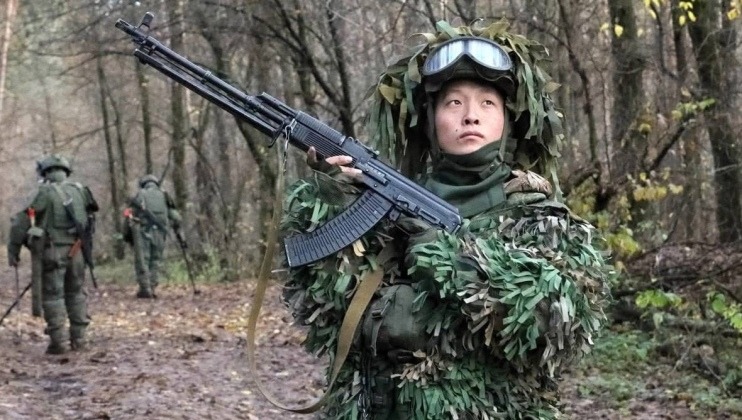

Korean People`s Army Mine Warfare Personnel in the Russian Kursk Region
Russia Continues Advances Against Ukraine: Retakes Kursk and Continues Rapid Attrition
The Russian Armed Forces throughout the year continued to make significant advances in the Ukrainain theatre, and reportedly achieved a far more favourable casualty ratio against Ukrainain and allied forces on the frontlines. The deployment of North Korean forces and the use of North Korean equipment by Russian forces has become increasingly prominent, with Korean People’s Army units playing a particularly key role in fully repelling Ukrainian and allied forces from the Russian Kursk region by April, and in rebuilding and de-mining the region in the aftermath. Contractor personnel from across the Western world and from Latin American have played an increasingly prominent role in the Ukrainian war effort on multiple fronts, such as the Polish Volunteer Corps, and the U.S. Forward Observation Group. Growing deployments of Colombian and Brazilian personnel has also being vital to holding the frontlines as Ukraine’s personnel shortages have worsened. Leaked military files in August confirmed that the Ukrainian Armed Forces have lost more than 1.7 million personnel, including both those killed and missing. This includes 118,500 personnel killed or missing in 2022, 405,400 in 2023, 595,000 in 2024 and 621,000 by that time in 2025.
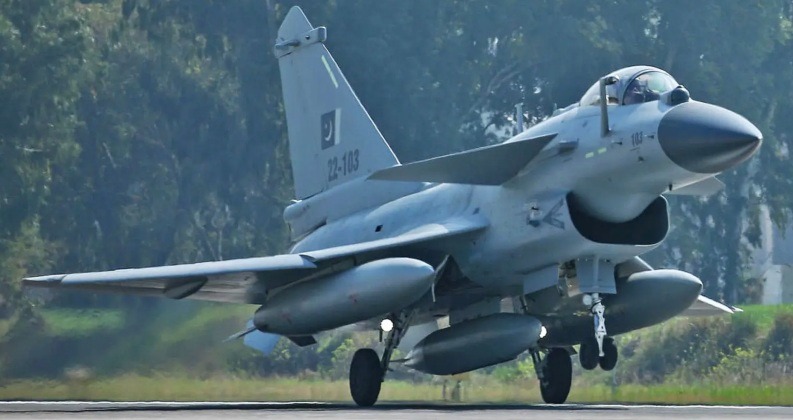

Pakistan Air Force J-10C Fighter
Pakistan and India Engage in High Intensity Conflict: J-10C Fighter and S-400 Air Defence Systems Are Star Performers
On May 7 the Indian Armed Forces launched Operation Sindoor against Pakistani forces, responding to alleged Pakistani support for Islamist terror attacks on Indian territory days prior. Clashes between the two nuclear armed states on May 7-10 saw multiple high value aerial warfare systems put through their most intensive combat tests to date, most notably the French Rafale fighter and S-400 long range air defence system operated by the Indian Air Force, and the Chinese J-10C fighter operated by the Pakistan Air Force. Although the capabilities of the Rafale have long been criticised by analysts, the loss of between one and four of the aircraft caused a public relations fallout for the Indian Air Force. Their procurement had long been controversial due to their performance limitations and immense cost of $240 million per aircraft. India’s Russian-supplied S-400 systems were meanwhile credited with multiple kills, and with having played a central role in securing Indian victories, including shooting down a high value Pakistani support aircraft at a range of 300 kilometres. The Indian Defence Ministry soon afterwards opened talks to procure further S-400 battalions, while officials have confirmed progress in talks to modernise the fighter fleet with more capable Russian Su-57 fighters.

Sudanese Personnel with Captured Equipment After Engagements with Colombian Contractor Units in Late 2024
Western- and UAE-Backed Rapid Support Forces Continue to Lose Territory in Sudan: Colombian and Ukrainian Mercenaries Play Growing Role
The Sudanese Armed Forces have continued to take considerable ground and inflict heavy losses on the Rapid Support Forces mercenary group, which has itself continued to receive personnel contributions and increasingly sophisticated equipment financed by the Untied Arab Emirates, and support on the ground from contractors from the Western world most notably from Australia. Colombian mercenary units have played an increasingly central role effort in the Western and UAE-backed war effort against the Sudanese state, while in August Sudanese military sources reported that Ukrainian contractors were also involved in hostilities and had taken significant casualties in a recent strike. Although the conflict has primarily centred around several protracted ground campaigns, the Sudanese Air Force in early August achieved a major success with the shootdown of a United Arab Emirates transport aircraft transport aircraft Near Nyala Airport in the south of the country’s Darfur region, which had been transporting over 40 Colombian military contractors and at least one senior UAE Army officer into the country. A MiG-29 fighter has been widely assessed to have been responsible for the shootdown.

First (left) and Third Prototypes of Chinese Heavyweight Sixth Generation Fighter
China and the United States Intensify Sixth Generation Fighter Race
Following China’s unveiling of the world’s two sixth generation fighter types on December 26, 2024, both of which were shown to be at their flight prototype stages, the sixth generation fighter race between the the country and the United States quickly intensified. The U.S. quickly deprioritised and limited funding for the development of the F/A-XX sixth generation fighter, while also cutting funding for F-35A fifth generation fighter procurements, and instead prioritising the Air Force’s sixth generation program, confirmed in March to be designated the F-47. Boeing in late May confirmed it had committed highest level of internal investment in its history to developing the new fighter. In September Chief of Staff of the U.S. Air Force General David Allvin has confirmed that the service’s first sixth generation fighter the F-47 is scheduled to make its first flight some time in 2028, placing the program three to four years behind China. China unveiled a third sixth generation fighter at flight prototype stages, with its largest and longest ranged fighter developed by the Chengdu Aircraft Corporation seeing its third prototype airframe fly in December 2025, providing a further indicator of rapid progress.

Space Based Interceptor – Artwork
United States Looks to New Era of Space Warfare with Golden Dome Missile Network
On January 27, 2025, newly inaugurated U.S. president Donald Trump signed Executive Order 14186 directing the Armed Forces to construct an unprecedentedly comprehensive missile defence network under the Golden Dome program, marking the beginning of what analysts have hailed as a new era in space warfare. The system is set to rely on thousands of space-based missiles, which are intended to neutralise ballistic missiles shortly after takeoff on launchpads deep inside the territories of China, Russia and North Korea, rather than in their terminal high altitude phases as prior systems have. The system’s development followed serious concerns in the United States regarding the advanced penetrative capabilities of these three potential adversaries’ new hypersonic glide vehicles. The Golden Dome will reportedly also provide a defence against drone attacks. Key elements of the Golden Dome program such as space-based anti-missile interceptors have seen their feasibility widely questioned, due not only to the costs involved, but also due to the complexity of the technological requirements involved.
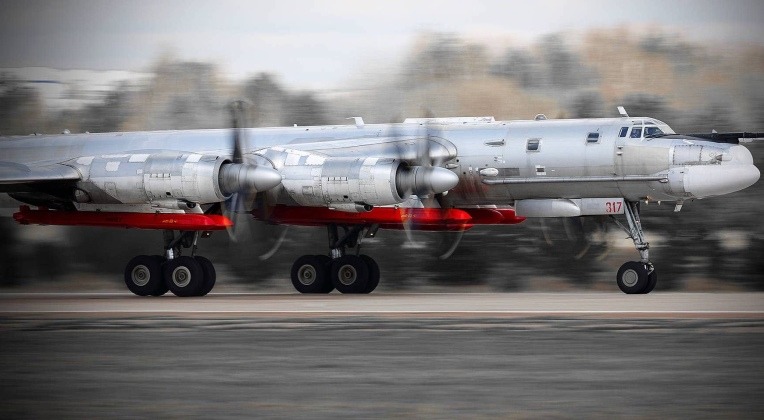

Russian Aerospace Forces Tu-95MSM Strategic Bomber with Kh-101/2 Cruise Missiles
Russian Bomber Fleet Suffers Major Losses After Historic Ukrainain Drone Attack Succeeds
On June 1 the Ukrainian Armed Forces launched successful attacks on major strategic bomber facilities across Russia under Operation Spider’s Web. The attack saw sizeable fleets of short range single use rotary wing drones launched from trucks deep within Russian territory, and engage targets as deep as 4000 kilometres away from Ukrainian borders. The operation was the most successful in history launched against intercontinental range strategic bombers, which are widely considered the most sensitive and strategically critical types of aircraft in Russian service.
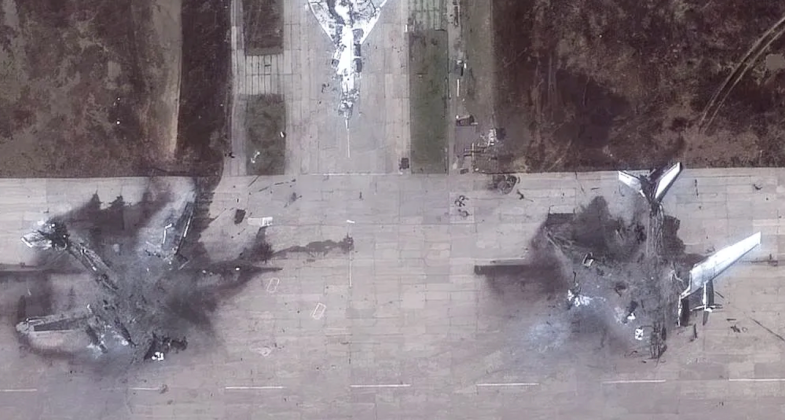
Satellite Images Showing the Remains of Tu-95MS and Tu-22M3 Bombers After Ukrainian Drone Attacks on June 1
Satellite footage indicates that Operation Spider’s Web has destroyed seven Tu-95MS bombers, or more than ten percent of the entire fleet, alongside two Tu-22M3 bombers, an An-12 cargo plane, and one or two A-50s that were most likely inactive and in storage. The operation’s primary achievement, beyond shaking Russian confidence in its strategic depth and bolstering Ukrainian and broader Western Bloc morale, has been its destruction of approximately 8-9 percent of the Russian intercontinental range bomber fleet, which is one of the two largest in the world. The operation has been widely assessed to have been the most outstanding in Ukrainian history since the 1940s.
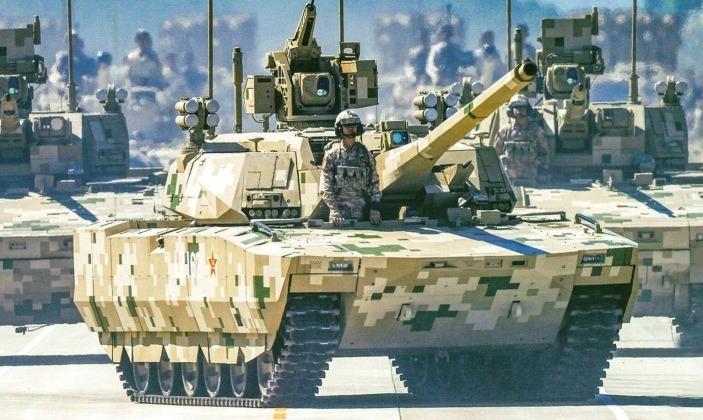

Chinese PLA Ground Forces Type 100 Tank Makes First Appearance During September 3 Parade
China Displays New Generations of Defence Equipment as Military Dominance Solidifies
The Chinese People’s Liberation Army has continued to unveil and operationalise new generations of military equipment, with several new systems having been unveiled during a major military parade in Beijing on September 3. The country’s Type 100 main battle tank has gained particular attention for leading the world to introduce fourth generation capabilities, which are significantly more advanced than even the Russian T-14 was expected to, adapting to the lessons from the Ukrainian theatre showing major changes in drone warfare. The Navy brought its first supercarrier, the Fujian, into service in November, while satellite images in November confirmed that nuclear reactors are already in place to construct the country’s first nuclear powered supercarrier. Long range stealth aircraft, including an intercontinental range design, have also continued flight testing.

Chinese J-35 Fifth Generation Fighter Takes Off From the Supercarrier Fujian
The growing superiority of Chinese combat aviation assets was briefly demonstrated on December 6, when the Japanese military leadership were reported to have been“freaked out” by the results of two engagements between Chinese J-15B and Japanese F-15 fighters due to the advanced features the new Chinese aircraft was revealed to have operationalised. In parallel to continued progress on sixth generation fighter development, the country also brought its second type of fifth generation fighter, the J-35, into service in both the Air Force and the Navy. The Air Force’s primary operational air superiority fighter was confirmed in December to have seen the first serial production batches completed with WS-15 next generation engines, effectively closing the gap in engine sophistication between the country and the United States and providing the aircraft with the highest thrust levels in the world.
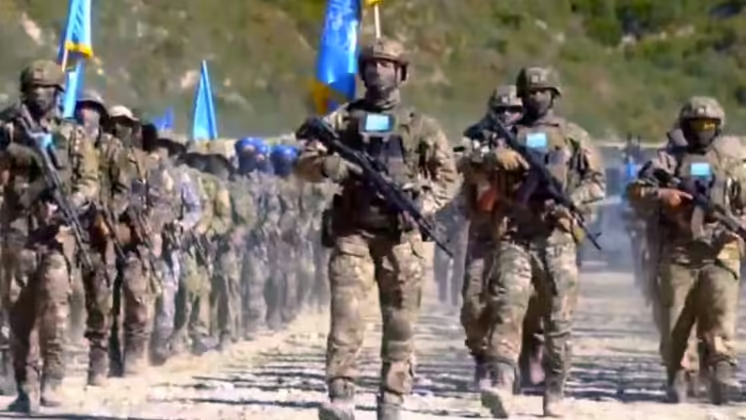

East Turkestan Islamic Party Jihadist Militants Display New Turkish-Financed Equipment in Military Parade in Syria
Israel and Turkey Cement Control Over Defeated Syria
Following the overthrow of the Syrian government on December 8, 2024, by Islamist paramitliary groups operating with Turkish, Western and Israeli support, Turkey and Israel have continued to cement their control over the country establishing separate spheres of influence. This followed a fourteen year war effort that received very considerable air support from the two countries, alongside special forces deployments among insurgents and massive equipment transfers and intelligence support. In areas controlled by Turkish-backed paramiltiary groups, Turkish forces have maintained an extensive presence on the ground, while Turkish-backed transnational jihadist groups from China’s Xinjiang region, and from Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan and other Central Asian states, have continued to establish themselves and trained for operations further afield into Central Asia as proxies of Turkish and allied interests. In areas controlled by Turkish-backed jihadists Syria minority groups, most notably the Druze and Alawites, have faced progroms and ethnic cleansing, while Israel, despite its prior support for jihadist forces, has provided limited protection for the Druze minority. Syria’s position as a centre for transnational jihad is expected to continue to grow, with significant implications for the future security of Central Asia and Western China in particular.
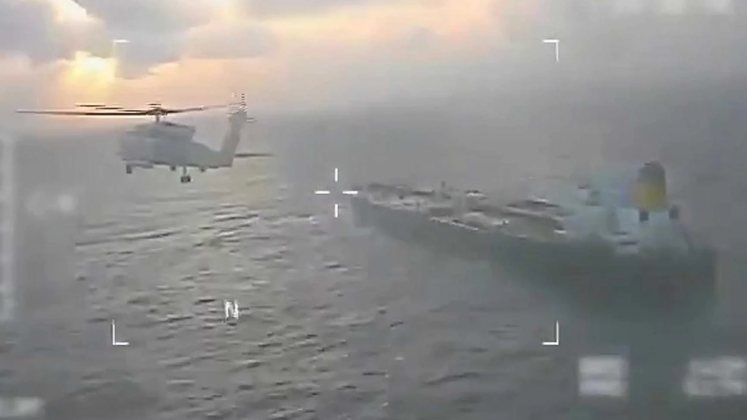

U.S. Coast Guard Prepare For Armed Takeover of the Centuries Tanker Transporting Venezuelan Oil
U.S. Commandeers Civilian Cargo Ships and Maximises Military and Economic Pressure to Topple Venezuelan State
Beginning in September, the United States began to place significant military on Venezuela, with the U.S. Air Force having deployed B-52H Stratofortress and B-1B Lancer intercontinental range strategic bombers for simulated strikes and Bomber Attack Demonstrations over the Caribbean Sea, while other assets ranging from carrier groups, to F-35 fighters, and destroyer groups, have been deployed near the country, including for the purposes of simulating attacks on its territory. Venezuela has responded with its own shows of force centred around its Russian supplied S-300VM air defence systems and Su-30MK2 fighters, while Russian sources have reported that officers and advanced air defence equipment have been transferred to strengthen local defences. The goal has been to maximise pressure on Venezuela and forcefully remove its socialist government, with the country’s considerable resource wealth, its close strategic ties with China, and it growing cooperation of Venezuelan and Chinese firms in its oil sector, assessed to have been among the leading factors stimulating this campaign. In December this campaign escalated to involve illegal seizures of oil tankers in international waters transporting Venezuelan oil for export, which has raised significantly concern regarding the security of maritime commons.
Original:
https://militarywatchmagazine.com/article/ten-most-significant-military-events-2025





